Source Editor
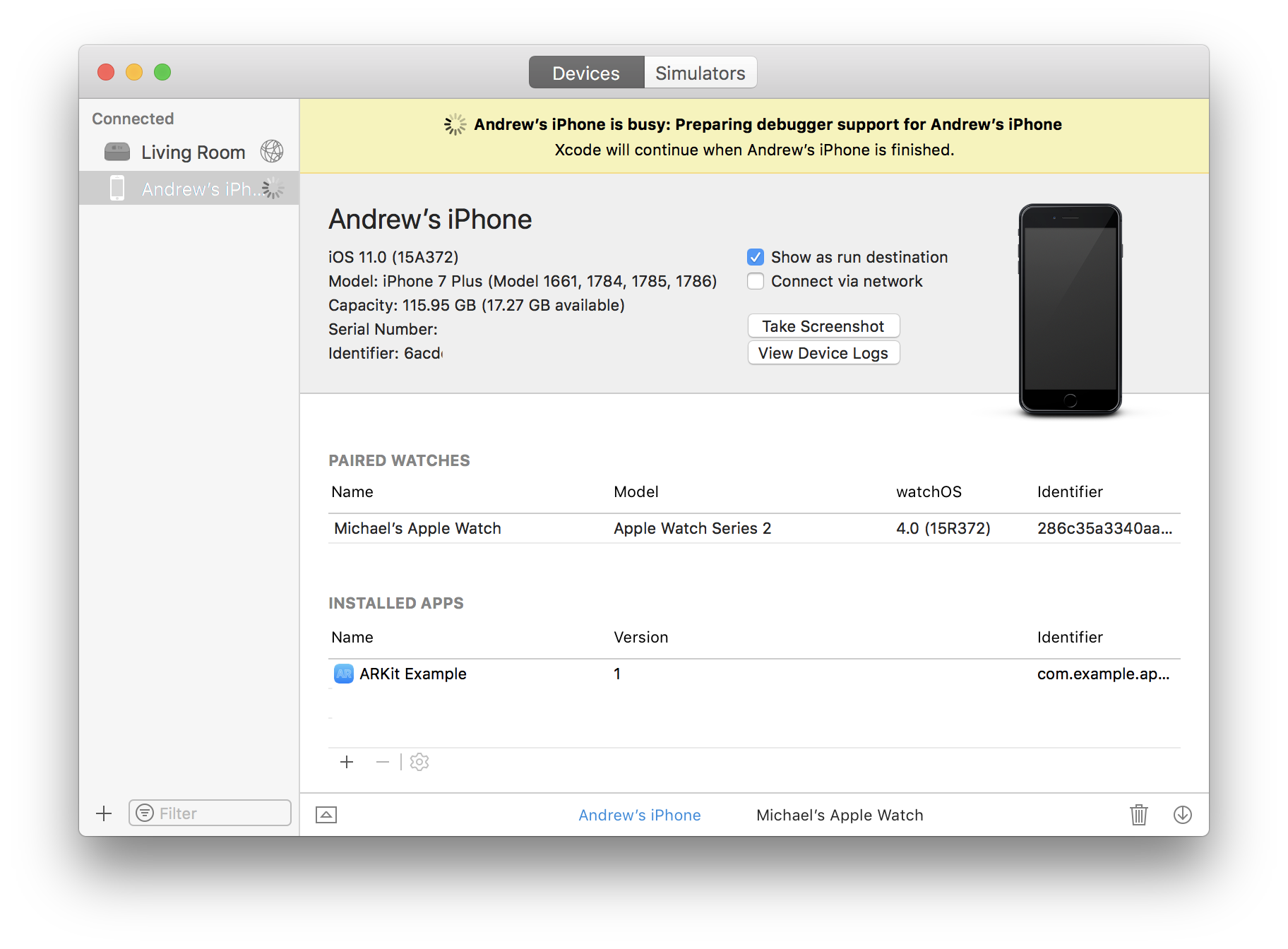
Building your app to a iOS device involves two steps: Unity builds an Xcode project. Xcode builds that project to your device. To select the device that Xcode builds to, follow these steps: Connect the device to your computer. From Xcode's main menu, go to Product Destination, and select your device from the Devices. Open up a project in Xcode and click on the device near the Run ▶ button at the top left of your Xcode screen. Plug your iPhone into your computer. You can select your device from the top of the list. Unlock your device and (⌘R) run the application. Steps To Trust The Xcode App In iPhone. Click General — Settings — Device Management menu item in iPhone device. The Device Management menu item only appear when you run the Xcode app on the iPhone. Click the app in the DEVELOPER APP section. Click the Trust button in the next screen. Then you can run the Xcode project app in your iPhone.
Write code using a professional editor with advanced code completion, code folding, syntax highlighting, and message bubbles that display warning, errors, and other context-sensitive information inline with your code.
Assistant Editor
The Assistant button splits the editor in two, creating a secondary pane that automatically displays files that are most helpful to you based on the code you are actively editing. It can show the header counterpart, the superclass, callers, callees, or other helpful files.
Version Editor
Xcode's Version editor displays a running timeline of commits, helps you determine blame, and graphically goes back in time to compare source files, with full support for Subversion and Git source control (SCM) systems.
Interface Builder Built-In
Design and test your user interface without writing a line of code, prototype in minutes, then graphically connect your interface to the source within the Xcode editor.
Simulator
With the iOS SDK, Xcode can build, install, run, and debug Cocoa Touch apps in a Mac-based Simulator for a streamlined development workflow.
Integrated Build System
Handles the most complex builds, scaling to maximize the power of multi-core Macs, and will automatically sign, provision, and install iPad and iPhone apps onto a device.
Compilers
The powerful open-source LLVM compiler for C, C++, and Objective-C is built into Xcode and available from Terminal. With it, your code compiles quickly, and is optimized by Apple to produce blazing-fast apps specifically tuned for the CPUs in iPhone, iPad, and Mac.
Connect Device To Xcode Install
Graphical Debugger
Debug your app directly within the Xcode editor. Hover over any variable to drill into its contents, use Quick Look to see the data it contains, or right-click to add the variable to the watch list.
Continuous Integration
Xcode Server controls server-side bots that continuously build, analyze, test, and even archive your Xcode projects. The Xcode IDE configures these bots, analyzes nightly build and test results, and can track down which check-in broke the build.
Asset Catalog
The asset catalog editor in Xcode manages your app's images, grouping together various resolutions of the same asset. When building, Xcode compiles the asset catalog into the most efficient bundle for final distribution.
Open Quickly
Simply press Cmd-Shift-O to instantly open any file within your workspace using the primary editor, or hold the Option key when selecting a file to open it in the Assistant editor. Open Quickly is an essential tool in any keyboard-driven workflow.
OpenGL Frame Capture
Press a single button to capture a complete representation of the current OpenGL frame from an iOS device. Xcode displays the shader information, and can visually construct how the frame was assembled within the Xcode debugger.
Complete Documentation
Easily search and find anything within Help or the Documentation and API Reference viewer.
Live Issues
Just like a word processor highlights spelling errors, Live Issues highlights common coding mistakes, without the need to click ‘build' first.
Fix-it
Xcode goes beyond just reporting errors. When you make a coding mistake, Xcode will immediately alert you, and a single keyboard shortcut will instantly fix the issue, so you won't miss a beat while coding.
Quick Help
Shortened API documentation is displayed while you're programming, including comments that you write for your code. A brief overview is presented during code completion, with more links and references available within the Utility area.
XCTest Framework
XCTest APIs make it easy to build unit tests that exercise app functionality and are capable of running on Mac, iPad, iPhone, or Simulator.
Static Analysis
Find bugs in your code before the app is even run by letting the built-in static analyzer try out thousands of possible code paths in a few seconds. You'll get a report of potential bugs that could have remained hidden or are nearly impossible to replicate.
Declarative syntax
Write simpler code with a declarative Swift syntax that clearly states what your user interface should do.
Design tools

Version Editor
Xcode's Version editor displays a running timeline of commits, helps you determine blame, and graphically goes back in time to compare source files, with full support for Subversion and Git source control (SCM) systems.
Interface Builder Built-In
Design and test your user interface without writing a line of code, prototype in minutes, then graphically connect your interface to the source within the Xcode editor.
Simulator
With the iOS SDK, Xcode can build, install, run, and debug Cocoa Touch apps in a Mac-based Simulator for a streamlined development workflow.
Integrated Build System
Handles the most complex builds, scaling to maximize the power of multi-core Macs, and will automatically sign, provision, and install iPad and iPhone apps onto a device.
Compilers
The powerful open-source LLVM compiler for C, C++, and Objective-C is built into Xcode and available from Terminal. With it, your code compiles quickly, and is optimized by Apple to produce blazing-fast apps specifically tuned for the CPUs in iPhone, iPad, and Mac.
Connect Device To Xcode Install
Graphical Debugger
Debug your app directly within the Xcode editor. Hover over any variable to drill into its contents, use Quick Look to see the data it contains, or right-click to add the variable to the watch list.
Continuous Integration
Xcode Server controls server-side bots that continuously build, analyze, test, and even archive your Xcode projects. The Xcode IDE configures these bots, analyzes nightly build and test results, and can track down which check-in broke the build.
Asset Catalog
The asset catalog editor in Xcode manages your app's images, grouping together various resolutions of the same asset. When building, Xcode compiles the asset catalog into the most efficient bundle for final distribution.
Open Quickly
Simply press Cmd-Shift-O to instantly open any file within your workspace using the primary editor, or hold the Option key when selecting a file to open it in the Assistant editor. Open Quickly is an essential tool in any keyboard-driven workflow.
OpenGL Frame Capture
Press a single button to capture a complete representation of the current OpenGL frame from an iOS device. Xcode displays the shader information, and can visually construct how the frame was assembled within the Xcode debugger.
Complete Documentation
Easily search and find anything within Help or the Documentation and API Reference viewer.
Live Issues
Just like a word processor highlights spelling errors, Live Issues highlights common coding mistakes, without the need to click ‘build' first.
Fix-it
Xcode goes beyond just reporting errors. When you make a coding mistake, Xcode will immediately alert you, and a single keyboard shortcut will instantly fix the issue, so you won't miss a beat while coding.
Quick Help
Shortened API documentation is displayed while you're programming, including comments that you write for your code. A brief overview is presented during code completion, with more links and references available within the Utility area.
XCTest Framework
XCTest APIs make it easy to build unit tests that exercise app functionality and are capable of running on Mac, iPad, iPhone, or Simulator.
Static Analysis
Find bugs in your code before the app is even run by letting the built-in static analyzer try out thousands of possible code paths in a few seconds. You'll get a report of potential bugs that could have remained hidden or are nearly impossible to replicate.
Declarative syntax
Write simpler code with a declarative Swift syntax that clearly states what your user interface should do.
Design tools
Drag and drop to construct or edit your interface. Quickly make changes to visual UI elements with pop-up inspectors.
Native on all Apple platforms
Your apps gain incredible native performance and take advantage of the proven technologies, controls, and user experiences of Apple platforms to feel fully integrated.
Live mode
See your design change instantly in one or many exact previews. Switch the design canvas to live mode to instantly interact with your running app in Xcode or on a connected device.
Data Recording
Tell Instruments which app to analyze, what type of data to collect, and simply click the big red button as data is collected and stored for further analysis.
Visual Comparison
As data is recorded and displayed over time it is easy to see relationships, both between different types of collected data, or the same data collected over multiple runs.
Drill Down
Inspect data spikes on the graph to see what code is executing at the time, then easily jump into Xcode to fix the problem.
Instrument Library
Choose any of the bundled instruments in the library from low-level CPU, network, or file activity, to advanced graphics and user-event instruments.
Connect Device To Xcode Sync
Zombie Detection
Hard-to-find errors and crashes can be trapped within Instruments when an app tries to access memory that is no longer available.
Source View
Drill down through data points, sort to find the most CPU-consuming methods, and view the code directly within the Instruments UI to pinpoint the problem.
Low-Overhead Sampling
Sample performance data with a simple key press, using low overhead to collect high-fidelity information.
Custom Instruments
Create your own Instruments using DTrace and the Instruments custom builder.
System Trace
Taking up very few resources, Instruments records information about all the processes on your system, revealing performance bottlenecks caused as processes interact.
Command Line Tools
Download the macOS SDK, headers, and build tools such as the Apple LLVM compiler and Make. These tools make it easy to install open source software or develop on UNIX within Terminal. macOS can automatically download these tools the first time you try to build software, and they are available on the downloads page.
Script languages
macOS comes with AppleScript, Perl, Python, and Ruby already installed. And because macOS is built on UNIX, you can easily build your versions of popular open source languages using Xcode or the command line developer tools that come with macOS.
Apple Event Bridge
AppleScript and Automator get much of their power from the underlying Apple Event engine, making it easy to automate tasks on macOS. This bridge lets you command and query apps from additional languages such as Objective-C, Ruby, and Python, using the same messaging architecture as AppleScript.
Audio Tools
The AU Lab tool enables mixing and manipulation of audio streams.
Terminal 2
Terminal 2 provides access to the UNIX shell with tabs, colors, and Unicode support.
Source Control: Git and Subversion
The Xcode IDE supports both of these SCM systems directly within the IDE, and makes them available from the command line.
UNIX tools
These include all of the most popular command line tools such as make, awk, sed, ssh, tar, and zip.
Editors
The editors in macOS include TextEdit, xed (the Xcode editor), plus vim and emacs.
FileMerge
Compare, differentiate, and merge any text document.

